body

Source: www.cell.com
Introduction: Why daily habits mater for immunity
Imagine waking boost immunity with nutrition and up each morning knowing your body has all it needs to resist infections, recover faster, and keep energy levels steady throughout the day. Your immune system isn’t an on/off switch — it’s a dynamic network that responds to what you eat, how you move, how you sleep, and how you manage stress. Small, consistent changes in nutrition and exercise compound over time and deliver real protection.
In this article you’ll learn actionable wellness tips, discover top immunity-boosting foods, build a realistic daily exercise routine, and adopt lifestyle strategies designed to nurture your immune defenses. Whether you’re a busy parent, a desk-bound professional, or someone starting a healthier path, this guide gives the tools to create sustainable habits that support long-term vitality.

What you’ll find in this guide
-
-
- Core nu boost immunity with nutrition trition strategies and a list of immunity-boosting foods
- A practical daily exercise routine for immune support
- Daily schedule examples and meal templates
- Stress management, sleep, and other healthy lifestyle tips
- Action plan, FAQs, internal/external link suggestions, and social sharing ideas
-

How nutrition directly affects your immune system
Your immune system relies on nutrients to build cells, produce antibodies, and regulate inflammation. Deficiencies or inconsistent intake of key vitamins, minerals, and macronutrients weaken immune responses. Eating a variety of whole foods — especially fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, healthy fats, and fermentable fibers — gives your body the building blocks it needs.
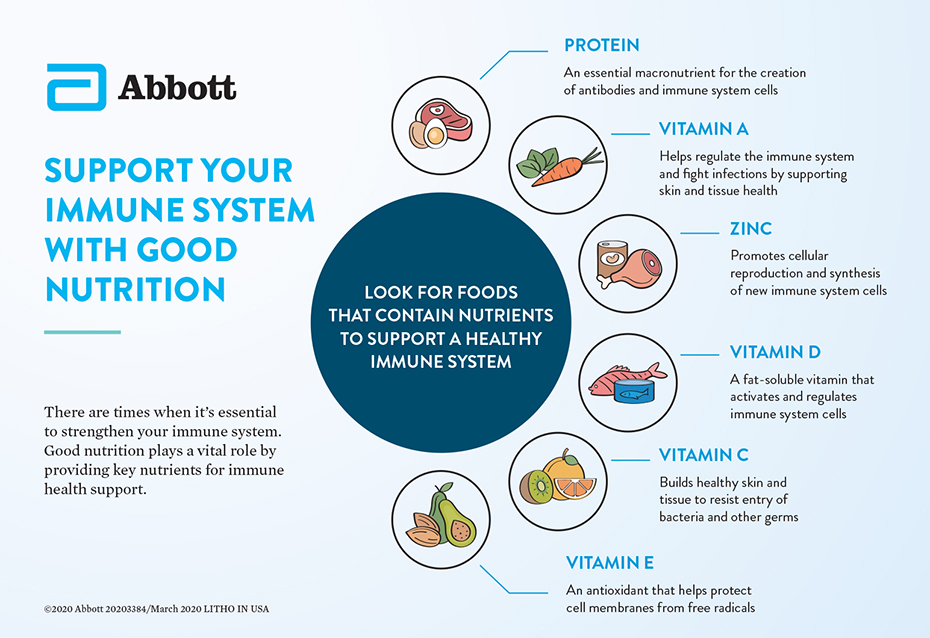
Key nutrients that support immunity
- Vitamin C: Supports white blood cell function and antioxidant protection.
- Vitamin D: Modulates immune response; deficiency is linked to higher infection risk.
- Zinc: Critical for immune cell development and pathogen defense.
- Protein: Essential for antibodies, immune signaling molecules, and repair.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Help regulate inflammation and support cell membrane health.
- Probiotics & prebiotic fiber: Maintain gut microbiome balance, which strongly influences immunity.
- Antioxidants (vitamin E, polyphenols): Protect immune cells from oxidative damage.
Top immunity-boosting foods to include daily
Focus on whole, minimally processed foods that deliver the nutrients above. Below is a practical list to rotate through your weekly meals.
| Food | Benefits | How to use daily |
|---|---|---|
| Citrus fruits (oranges, grapefruits) | High in vitamin C | Breakfast fruit or mid-morning snack |
| Berries (blueberries, strawberries) | Antioxidants & polyphenols | Smoothies, yogurt topping, oatmeal |
| Leafy greens (spinach, kale) | Vitamins A, C, folate, fiber | Salads, sautés, smoothies |
| Cruciferous veggies (broccoli, Brussels) | Vitamin C, fiber, sulforaphane | Roast, steam, stir-fry |
| Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel) | Omega-3s, vitamin D | 2–3 servings/week or use canned fish |
| Lean protein (chicken, turkey, legumes) | Protein for antibodies and repair | Include in lunch and dinner |
| Nuts & seeds (almonds, walnuts, chia) | Healthy fats, vitamin E, zinc | Snacks, yogurt, salads |
| Yogurt & fermented foods (kefir, kimchi) | Probiotics for gut health | Daily spoonful or serving |
| Garlic & onions | Antimicrobial compounds & immune support | Add to cooking frequently |
| Mushrooms (shiitake, maitake) | Beta-glucans that modulate immunity | Soups, sautés, stir-fries |
Meal pattern suggestions for immune support
Rather than strict rules, follow patterns that ensure variety and micronutrient coverage.
- Breakfast: Protein + fruit + whole grain/fiber + healthy fat (e.g., Greek yogurt with berries and chopped nuts).
- Lunch: Vegetables + lean protein + whole grain (e.g., spinach salad with salmon and quinoa).
- Snack: Fermented food or nuts + piece of fruit.
- Dinner: Non-starchy vegetables + protein + healthy fat (e.g., stir-fried broccoli with tofu and sesame).
Daily exercise routine to strengthen immunity
Exercise is one of the most consistent ways to support immune function. Regular moderate exercise improves circulation, reduces inflammation, enhances immune cell recruitment, and improves sleep and mood.
Principles for an immunity-friendly exercise plan
- Aim for consistency: shorter daily workouts beat occasional intense sessions for immunity.
- Moderate intensity is best: brisk walking, cycling, or light resistance training for 30–60 minutes most days.
- Include strength training 2–3 times weekly to preserve muscle and metabolic health.
- Prioritize recovery: sleep, hydration, and nutrition around workouts matter.
Sample daily exercise routine (30–45 minutes)
- Warm-up (5–7 minutes): Joint rotations, brisk walking, dynamic stretches.
- Cardio (20–25 minutes): Brisk walk, cycling, swimming, or interval walking (1–2 min faster pace, 2 min easy).
- Strength (10–12 minutes): Two circuits of bodyweight or light weights — squats, push-ups, lunges, rows, planks (8–12 reps each).
- Cool-down & mobility (3–5 minutes): Gentle stretching, diaphragmatic breathing.
Short routines for busy days (10–15 minutes)
- Tabata-style: 20 seconds work / 10 seconds rest — choose 4 moves (squats, mountain climbers, push-ups, jumping jacks) for 4 rounds.
- Walk + mobility: 10-minute brisk walk + 5 minutes of targeted stretches.
- Strength micro-workout: 2 sets of 10–15 squats, glute bridges, push-ups, and plank holds.
How exercise intensity affects immunity
Moderate exercise enhances immune surveillance and reduces inflammation. Very intense, prolonged training without adequate rest can temporarily suppress immune function and raise infection risk. Aim for a balance: challenge yourself but build in recovery and sleep.
Daily schedule: Combining nutrition and movement for maximum benefit
Here’s a realistic daily plan that integrates immunity-boosting foods, exercise, stress management, and sleep hygiene. Use it as a template and adapt to your life.
Daily example (weekday)
- 6:30 AM — Wake up; hydrate with a glass of water + squeeze of lemon.
- 7:00 AM — 20–30 minute moderate exercise (brisk walk or at-home circuit).
- 7:30 AM — Breakfast: Oatmeal with berries, chia seeds, and a spoonful of almond butter.
- 10:00 AM — Snack: Plain yogurt with a sprinkle of seeds or a small citrus fruit.
- 12:30 PM — Lunch: Mixed greens with grilled chicken, quinoa, roasted vegetables, olive oil dressing.
- 3:00 PM — Short walk or mobility break (5–10 minutes); snack: apple + handful of walnuts.
- 6:30 PM — Dinner: Baked salmon, steamed broccoli, sweet potato, side of fermented vegetables.
- 8:00 PM — Relaxation: light stretching, read, or deep-breathing exercises.
- 10:00 PM — Bedtime routine: dim lights, no screens 30 minutes before bed; aim for 7–9 hours sleep.
Stress management, sleep, and other lifestyle habits that support immunity
Nutrition and exercise are foundational, but stress and sleep strongly influence immune function. Chronic stress increases cortisol, which can dysregulate immune responses. Sleep is when immune repair and memory consolidation happen.
Daily habits for stress resilience and better sleep
- Practice 5–15 minutes of breathing, meditation, or progressive muscle relaxation daily.
- Keep a consistent sleep schedule — go to bed and wake up at similar times.
- Create a pre-sleep routine: dim lights, light stretching, limiting screen exposure.
- Limit alcohol and heavy meals close to bedtime.
- Social connection: maintain supportive relationships; even short daily check-ins boost well-being.
Hydration, gut health, and supplements — what to know
Staying hydrated supports mucosal barriers (nose, throat), which are the first line of defense. Gut health influences immune responses through the microbiome. Supplements can help when diet or testing reveals gaps, but they are not a replacement for a healthy lifestyle.
Hydration tips
- Drink water regularly; a simple cue is a glass before each meal.
- Include herbal teas and broths for variety and electrolytes if exercising heavily.
Gut-friendly practices
- Eat fermentable fibers (onions, garlic, leeks, legumes) and fermented foods regularly.
- Limit unnecessary antibiotics and take probiotics when recommended by a clinician after antibiotic use or for chronic gut issues.
Supplement guidance (general recommendations)
- Vitamin D: Consider testing and supplementing if low; many adults require 1,000–2,000 IU daily or more based on lab results.
- Vitamin C: Useful during increased need; 200–500 mg daily is common in balanced diets.
- Zinc: Short-term use during illness can help; long-term high doses may cause issues — consult a healthcare provider.
- Probiotics: Strain-specific benefits exist; choose a reputable product and consult a clinician for chronic conditions.
Always consult your healthcare provider before starting supplements, especially if you have chronic conditions or take medications.
Practical tips to make these habits stick
Consistency beats perfection. Use behavior-change strategies to turn these recommendations into sustainable routines.
- Habit stacking: Attach a new habit to an existing one (e.g., do 10 squats after brushing teeth).
- Prepare ahead: Batch-cook immune-friendly meals and pre-cut vegetables.
- Use reminders: Set calendar alerts for movement breaks and bedtime routines.
- Track progress: Simple checklists or apps can reinforce consistency without judgment.
- Find an accountability partner or join a class for social motivation.
Real-world examples & mini case studies
These short scenarios show how different people can implement the habits above.
Case: Busy professional — “Lena”
Lena works long hours and finds it hard to exercise. She built a 20-minute morning walk plus 10-minute evening strength routine into her schedule and started prepping overnight oats with berries for breakfast. Within a month she felt more energetic and reduced her afternoon caffeine intake.
Case: Parent of young children — “Marcus”
Marcus uses family walks after dinner for movement and swaps sugary snacks for yogurt with fruit. He started adding garlic and mushrooms to family dinners and noticed fewer sick days across the household during cold season.
Case: Retiree focusing on mobility — “Ruth”
Ruth prioritizes balance and resistance training twice a week, adds fermented foods to her diet, and practices 10 minutes of evening breathing exercises. She reports better sleep and fewer lingering colds.
Common questions (FAQ) — quick answers for feature snippets
How quickly do these habits improve immunity?
Some benefits (better sleep, mood, circulation) can appear within days to weeks. Measurable changes in immune markers may take weeks to months of consistent behavior.
Are immunity-boosting foods enough or do I need supplements?
Whole foods supply most nutrients for a healthy immune system. Supplements can help when blood tests show deficiencies or during higher-risk periods, but they are not substitutes for a healthy lifestyle.
Can exercise ever weaken my immune system?
Intense, prolonged exercise without proper recovery can temporarily suppress immunity. For most people, regular moderate activity strengthens immune defenses.
What should I eat if I get sick?
Focus on hydration, easy-to-digest proteins (broth, yogurt), vitamin C-rich fruits, and foods that support gut health. Rest and consult a clinician when symptoms are severe or prolonged.
Action plan: 14-day kickstart to boost immunity
- Day 1: Add one serving of vegetables to every meal. Start a 15-minute daily walk.
- Day 3: Introduce a fermented food (yogurt, kefir, kimchi) daily.
- Day 5: Start a simple strength routine twice this week.
- Day 7: Cut back on added sugars and replace one sweet treat with fruit.
- Day 10: Add 5 minutes of daily breathing or meditation before bed.
- Day 14: Review progress, set three realistic habits to continue and celebrate small wins.
Internal and external link suggestions (SEO-friendly)
- Internal link suggestions (anchor text): “Healthy recipes for immune support” (link to site recipe category), “Beginner’s guide to strength training” (link to existing strength training article), “Sleep hygiene tips” (link to sleep resource).
- External authoritative links (open in new window): World Health Organization (https://www.who.int/) for general health guidance, National Institutes of Health — Office of Dietary Supplements (https://ods.od.nih.gov/) for
For more lifestyle tips, check out our Top 16 Healthy Foods List.
Learn more on Healthline.







