Unhealthy Food for Teeth: What You Need to Know to Protect Your Smile
Our diet plays a central role in maintaining oral health. While most people know the importance of brushing and flossing, fewer are aware of how specific foods impact their teeth. Certain types of food are particularly harmful to dental health, causing cavities, gum disease, and other oral issues. Understanding these foods and making mindful choices can help protect your smile and keep dental problems at bay. In this article, we’ll delve into the most common culprits in the world of “unhealthy food for teeth” and offer actionable tips to maintain a bright, healthy smile.
Why Certain Foods Are Bad for Teeth
Foods that are high in sugar, starch, or acid can harm the teeth in different ways. Here’s how:
- Sugar: Bacteria in the mouth feed on sugar, producing acids that erode enamel, leading to cavities.
- Starches: Starchy foods like bread and pasta often break down into sugar, which can stick to the teeth and cause decay.
- Acids: Acidic foods and drinks, such as citrus fruits and sodas, can wear down enamel over time, making teeth more susceptible to decay.
Let’s explore these in more detail, examining specific foods and their impacts on dental health.
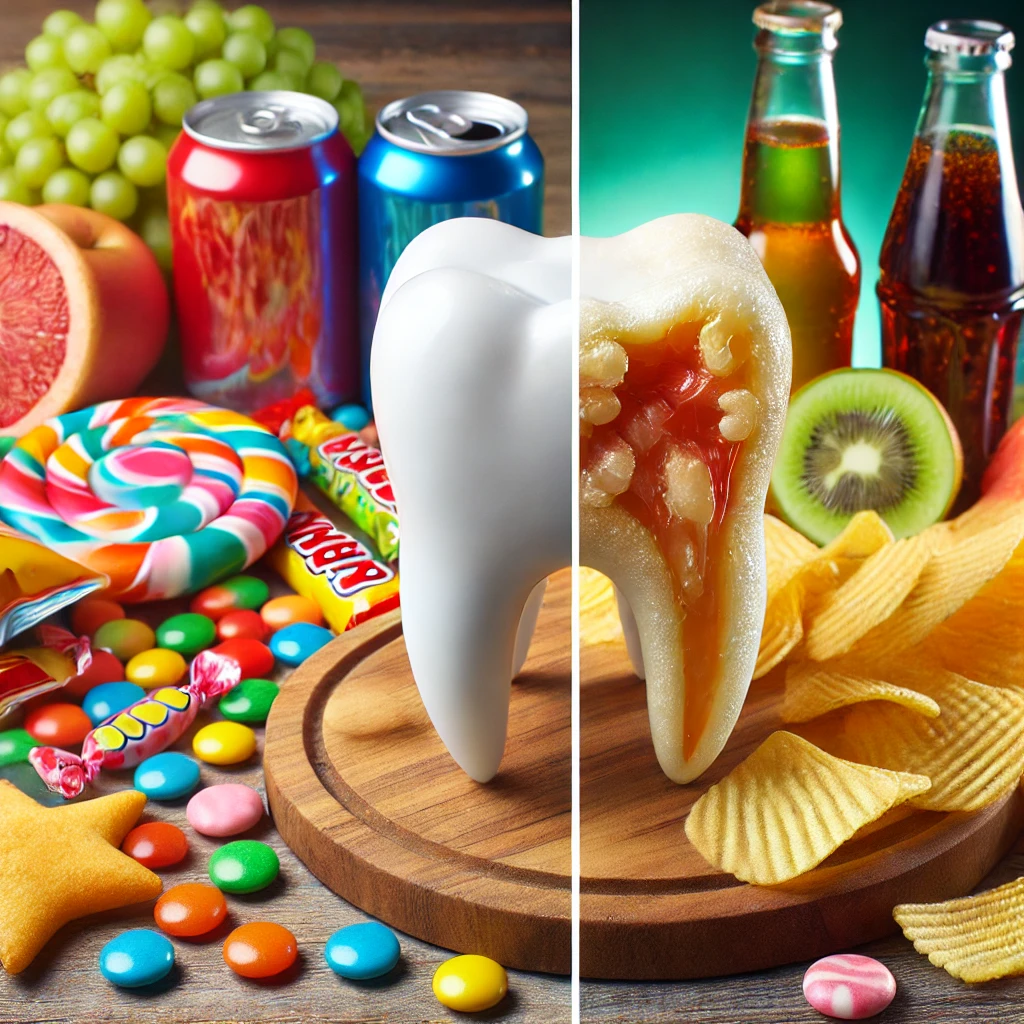
1. Sugary Treats: The Sweetest Danger

Examples: Candy, cookies, cakes, sugary drinks (soda, sweetened juices)
Sugary treats are among the biggest offenders when it comes to damaging teeth. Bacteria in the mouth, particularly Streptococcus mutans, consume sugar to create acids, leading to cavities. This is especially problematic with sticky sweets like caramels or gummies that cling to the teeth, allowing bacteria to feast on sugar for extended periods.
Real-World Impact
A 2016 study in Dental Research Journal found that children who consumed high-sugar diets had significantly more cavities than those with low-sugar diets. This correlation is not limited to children; adults who consume excessive sugar are at a similar risk for tooth decay and gum disease.
Actionable Steps
- Opt for Sugar-Free Alternatives: Choose sugar-free versions of candy and gum, which stimulate saliva production, helping to wash away food particles and acids.
- Limit Sweets to Mealtime: Saliva production is higher during meals, which helps to neutralize acids. Eat sweets as part of a meal rather than a snack to reduce their impact on teeth.
2. Starchy Foods: The Hidden Sugar

Examples: Bread, pasta, chips, crackers
Starchy foods often break down into sugars that feed bacteria in the mouth. Soft breads and chips, in particular, can become lodged in between teeth, creating an environment where bacteria thrive. The starch in these foods contributes to acid production, which can weaken enamel over time.
Real-World Impact
Studies have shown that starchy snacks can be as harmful to teeth as sugary snacks. Research published in Community Dentistry and Oral Epidemiology demonstrated that frequent consumption of starchy foods led to increased levels of plaque and tooth decay in adults.
Actionable Steps
- Choose Whole Grains: Whole-grain options have more fiber and take longer to break down into sugars, reducing their impact on teeth.
- Rinse with Water: After eating starchy foods, rinse your mouth with water to dislodge food particles and neutralize acid.
3. Acidic Foods and Beverages: Erosion of Enamel

Examples: Citrus fruits, vinegar-based foods, soda (both regular and diet), sports drinks
Acidic foods and beverages pose a double threat: they directly erode enamel, and they create an acidic environment in the mouth that allows harmful bacteria to thrive. The erosion of enamel is particularly problematic because, once lost, enamel doesn’t regenerate.
Real-World Impact
A study in the Journal of Dentistry found that people who frequently consumed acidic beverages had significantly more enamel erosion than those who didn’t. The effect was even greater among those who sipped these drinks slowly over time, which exposes teeth to acid for extended periods.
Actionable Steps
- Limit Exposure: Avoid sipping acidic drinks over a long period. Drinking them quickly minimizes the amount of time teeth are exposed to acid.
- Use a Straw: Drinking acidic beverages through a straw can help minimize contact with teeth.
- Rinse, Don’t Brush Immediately: After consuming acidic foods or drinks, wait at least 30 minutes before brushing. Brushing too soon can cause further enamel erosion.
4. Alcohol: Drying and Decaying
Examples: Beer, wine, spirits
Alcohol, especially in excess, can lead to dry mouth, reducing saliva production. Saliva is essential for neutralizing acids, washing away food particles, and maintaining healthy oral bacteria levels. Certain alcoholic beverages, like wine, are also acidic, further contributing to enamel erosion.
Real-World Impact
Research from the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition shows that regular alcohol consumption can increase the risk of gum disease and tooth decay. A dry mouth environment fosters bacterial growth, creating more acid that can lead to cavities.
Actionable Steps
- Drink Water Alongside Alcohol: Hydrating with water helps to rinse the mouth and stimulates saliva production.
- Opt for Less Acidic Choices: If you drink alcohol, consider less acidic options like beer or diluted spirits rather than wine, which is highly acidic.
5. Coffee and Tea: Staining and Decay

Examples: Coffee, black tea, flavored teas
Coffee and tea are notorious for staining teeth, but they also pose other risks. Both beverages can be acidic, and many people add sugar, enhancing the risk of decay. Additionally, coffee can dry out the mouth, contributing to a lower pH and promoting bacterial growth.
Real-World Impact
A study published in the International Journal of Dental Hygiene reported that regular coffee drinkers had more stains and higher levels of plaque than those who didn’t drink coffee.
Actionable Steps
- Drink Plain or Use Sugar Alternatives: Avoid adding sugar to coffee and tea. Stevia and other sugar substitutes are better choices for oral health.
- Rinse or Brush Afterward: If you’re a coffee or tea drinker, rinse your mouth with water afterward to minimize staining and acidity.
Case Study: The Impact of a High-Sugar, Acidic Diet
Consider the case of “Jake,” a 30-year-old office worker who developed cavities and gum disease after regularly consuming sugary snacks and energy drinks throughout his workday. Jake’s dentist observed significant enamel erosion and multiple cavities. Upon switching to water instead of energy drinks, reducing sugary snacks, and following a twice-daily brushing routine, Jake’s dental health improved noticeably within a year. His case illustrates the importance of diet choices in maintaining oral health.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is considered unhealthy food for teeth?Unhealthy food for teeth includes sugary snacks, acidic beverages, and starchy foods that can contribute to plaque buildup, enamel erosion, and cavities. Examples include candy, sodas, chips, and acidic fruits like lemons.
2. Why is sugar such an unhealthy food for teeth?Sugar is unhealthy food for teeth because it feeds harmful bacteria in the mouth. These bacteria produce acids that erode enamel, the protective layer of teeth, leading to cavities and decay.
3. Are acidic foods also considered unhealthy food for teeth?Yes, acidic foods are considered unhealthy food for teeth because they can wear down enamel over time. Foods like citrus fruits, vinegar-based dressings, and soda contribute to an acidic environment that damages teeth.
4. Is coffee an unhealthy food for teeth?Coffee can be considered unhealthy food for teeth due to its acidic nature, which can erode enamel. It also stains teeth and often contains added sugars or creamers that contribute to tooth decay.
5. Can starchy foods be classified as unhealthy food for teeth?Yes, starchy foods like bread, pasta, and chips can be unhealthy food for teeth. They break down into sugars, sticking to teeth and providing a food source for bacteria, which leads to acid production and potential tooth decay.
6. How does alcohol contribute to unhealthy food for teeth?Alcohol is considered unhealthy for teeth as it can dry out the mouth, reducing saliva production. Saliva is essential for neutralizing acids and washing away food particles, so less saliva can increase the risk of decay.
7. Are diet sodas also considered unhealthy food for teeth?Diet sodas are still considered unhealthy food for teeth due to their high acidity, which erodes enamel. Even though they don’t contain sugar, the acid in diet sodas can damage teeth over time.
8. Why are sticky candies particularly unhealthy food for teeth?Sticky candies are especially unhealthy food for teeth because they cling to tooth surfaces, allowing bacteria to feed on the sugars for longer periods. This prolonged exposure increases the risk of cavities and tooth decay.
9. Is dried fruit considered unhealthy food for teeth?Yes, dried fruit can be considered unhealthy food for teeth. While it’s often marketed as healthy, it contains concentrated sugars and has a sticky texture that adheres to teeth, which can lead to decay.
10. How can I reduce the effects of unhealthy food for teeth on my oral health?To reduce the effects of unhealthy food for teeth, try rinsing your mouth with water after consuming sugary or acidic foods, limit their frequency, and follow a regular dental hygiene routine that includes brushing and flossing.
Conclusion:
Protecting your teeth goes beyond daily brushing and flossing—it involves being mindful of the foods you consume. Sugary, starchy, and acidic foods contribute to a host of oral health issues, from cavities to gum disease. By reducing these foods in your diet, opting for healthier alternatives, and following simple protective strategies, you can significantly improve your dental health.
Key Takeaways
- Minimize Sugary and Acidic Foods: Sugar fuels bacteria, while acids erode enamel. Limiting these can reduce the risk of decay.
- Choose Tooth-Friendly Alternatives: Whole grains, sugar-free snacks, and water are great replacements.
- Follow Dental Hygiene Best Practices: Rinsing, waiting to brush after acids, and keeping hydrated all help protect your teeth.
By making informed choices and adopting a balanced diet, you can protect your smile and avoid common dental problems, ensuring better oral health for years to come.
For more insights into how a balanced diet can improve overall health, check out our Essential Health Foods Archives. Our comprehensive guides explore a variety of nutrient-rich foods that support both your hair health and overall well-being, helping you make smarter choices for a healthier lifestyle. Dive in to learn more about the foods that nourish your body from the inside out!.
For more information on how diet impacts oral health, you can explore additional insights on MedlinePlus. Their article, Dental Cavities – Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention, provides a comprehensive overview of dental cavities and offers practical tips for maintaining a healthy smile. This resource is valuable for anyone looking to deepen their understanding of dental care and the role of diet in preventing tooth decay.











⚡ Creative current! Sprunki conducts innovative energy.
Online slots like Super Ace are fun but come with risks. Always play responsibly and check site security before betting real money.
JiliPH stands out with its smooth gameplay and secure environment. I love the variety of slots like Fortune Gems and Money Coming. Check it out at JiliPH!
Roulette and slots both rely on luck, but games like Super Ace Jili add strategy with features like wilds and free spins. It’s exciting to see how math and design blend in modern slots.
Mobile gaming’s really evolving! Seeing platforms prioritize the experience is key – fast loading & intuitive design make all the difference. Check out PH987 Login for a streamlined mobile setup – it’s impressive how they’ve optimized everything for effortless play!
Solid analysis! Thinking about platform experience is key – it’s not just about the games, right? Seeing a focus on user feedback, like with PH987 casino login, really elevates things. Good service is a game changer! 👍
That’s a really insightful piece! Understanding the fundamentals is key – reminds me of resources like 26SuperPH Login, which breaks down complex gaming concepts step-by-step. Building that foundation is so important for sustainable skill development!